Introduction to Financial Instruments in Trade
In an increasingly interconnected global economy, financial instruments play a pivotal role in trade facilitation. These instruments serve as essential tools, enabling businesses to manage risks while engaging in international transactions. The complexity of trading across borders necessitates a deeper understanding of various financial instruments. In particular Standby Letters of Credit (SBLC) and Bank Guarantees (BG), which are prevalent in mitigating risks associated with trade agreements.

Financial instruments are formal contracts that represent a legal agreement involving monetary value. They can take many forms, including equity instruments, debt instruments, and derivatives, but in the context of trade, they primarily function as risk management tools. By providing credible assurance among trading parties, financial instruments enhance the reliability and efficiency of transactions.
Standby Letters of Credit, for instance, are guarantees issued by a bank on behalf of a client, intended to provide the beneficiary with recourse if the client fails to fulfill contractual obligations. This instrument effectively serves as a safety net, ensuring that payments will be made in case of non-performance. On the other hand, Bank Guarantees are commitments by a bank to cover a loss in case a client defaults. Both SBLC and BG are critical in establishing trust, reassuring parties involved in trade agreements that financial commitments will be honored.
Understanding these instruments is crucial for businesses in international trade, as they help secure transactions and enhance creditworthiness. The next sections explain SBLC and Bank Guarantees, outlining their structures, use cases, and trade-related implications. Therefore, gaining insight into these financial tools is essential for effective risk management and successful commercial operations today.
Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) Services
A Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) serves as a guarantee from a bank on behalf of a client, ensuring that the bank will fulfill a financial obligation if the client defaults. It is primarily utilized in international trade, functioning as a safeguard for sellers and buyers alike. When a buyer fails to make payment or fails to meet the obligations stipulated in the underlying contract, the seller can draw on the SBLC. This financial instrument enhances trust between parties engaged in trade, making it an essential component of transactions that might otherwise be deemed too risky.
The purpose of SBLC services extends beyond merely providing peace of mind. For businesses engaged in international commerce, an SBLC can be instrumental in facilitating trade, particularly with new partners or in unfamiliar markets. By offering an SBLC, buyers signal their credibility and commitment to fulfilling financial obligations. This not only fosters stronger business relationships but also allows sellers to feel secure in their dealings, knowing that they have a financial backup should the need arise.
Acquiring an SBLC involves a straightforward process, although businesses should be aware of key considerations. Firstly, entities must establish a relationship with a financial institution capable of issuing SBLCs. The terms of the SBLC, including its duration and coverage amount, should align with the specific trade requirements. Additionally, businesses must understand the associated costs, which may include both issuance fees and potential renewal costs. By carefully assessing these factors, businesses can maximize the benefits of SBLC services, ensuring that they are adequately protected in their trading endeavors.
Bank Guarantee (BG) Issuance
A Bank Guarantee (BG) is a financial instrument in which a bank assures a third party that a client’s specific obligation will be fulfilled. If the client defaults on their commitment, the bank is liable to pay a predetermined amount to the beneficiary. BGs are pivotal in international trade, as they foster trust between trading partners and mitigate risks associated with non-payment. They are also significant in providing security to sellers and facilitating smoother transactions.
The issuance of a Bank Guarantee involves several steps. Initially, the client seeking a guarantee must apply to their bank, providing necessary documentation that illustrates the purpose of the guarantee and the transaction details. This includes outlining the obligations or payment terms covered by the BG. After reviewing the application, the bank conducts a thorough due diligence process, assessing the applicant’s creditworthiness. Upon successful assessment, the bank issues the guarantee, which is then communicated formally to the beneficiary.
It is essential to understand the differences and similarities between Bank Guarantees and Standby Letters of Credit (SBLCs). Both instruments guarantee payment and support trade, but they meet different needs and serve distinct purposes. A Bank Guarantee assures the counterparty that payment will be honored if the principal defaults on obligations. Conversely, an SBLC acts as a secondary fallback, promising payment if a client fails to meet specific requirements.
Both instruments enhance security and trust but vary in structure and application within the trade ecosystem.
Financial Consulting Services
In trade finance, consulting services help businesses navigate complex instruments like Standby Letters of Credit (SBLC) and bank guarantees. These services help organizations create tailored financial strategies that match their specific operational needs and risks. By leveraging expert advice, companies strengthen their understanding of financial tools and improve their overall financial operations.
Financial consultants provide valuable insights into the intricate framework of trade finance. They assess each business’s unique needs, considering its industry, market conditions, and financial objectives. Through comprehensive analysis and structured planning, consultants can guide businesses in effectively utilizing various financial instruments. This ensures that organizations make well-informed decisions that facilitate smoother trade transactions and mitigate risks associated with international trade.
Moreover, these consulting firms often offer specialized knowledge regarding regulatory compliance and best practices in trade finance. Understanding legal and operational requirements is essential for businesses that want to operate efficiently and avoid potential pitfalls. Professional financial consultants stay current on global regulations and trends, helping businesses maintain compliance and adapt to change.
Additionally, financial consulting services provide ongoing support as companies implement their financial strategies. This ongoing relationship enables businesses to adjust their approaches based on performance assessments and market conditions. By continuously refining their financial operations, organizations can improve their profitability and competitive edge in the marketplace. Thus, engaging with financial consulting firms can significantly enhance a business’s capability to utilize financial instruments effectively.
Trade Finance Solutions
In the realm of international trade, companies often encounter challenges related to cash flow and risk management. Trade finance solutions play a crucial role in addressing these concerns, allowing businesses to optimize their operations while navigating the complexities of global markets. Various financial products are available to assist companies in maintaining liquidity and protecting against potential losses.
One significant solution is invoice financing, which allows businesses to access funds tied up in unpaid invoices. This method boosts cash flow, allowing companies to cover operational expenses without waiting for client payments. By leveraging receivables, businesses maintain financial health and secure the capital needed for growth and investment opportunities.
Another key product is trade credit insurance, which protects businesses from the risk of non-payment by international buyers. This insurance safeguards revenues and mitigates risks when expanding into new markets. With trade credit insurance, companies can confidently sign contracts and fulfill orders, knowing a safety net covers potential losses.
Factoring is another common trade finance option where businesses sell receivables to a third-party institution at a discount. This arrangement allows companies to receive immediate cash, improving cash flow and providing the flexibility needed to manage day-to-day operations. Factoring can be particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises that may struggle to secure traditional financing methods.
Overall, these trade finance solutions, including invoice financing, trade credit insurance, and factoring, equip businesses with the necessary tools to enhance cash flow, manage risks, and foster sustainable growth amid the complexities of international trade.
Monetization of Financial Instruments
Monetizing financial instruments like SBLCs and Bank Guarantees means converting them into cash or liquid assets for businesses. This process lets companies improve cash flow by leveraging the inherent value of these instruments as collateral or guarantees.
The monetization process typically involves engaging a financial institution or a specialized company to assess the value of the financial instrument. Once the valuation is established, the institution may offer liquidity in exchange for the instrument, often involving a discount. This method allows businesses to access funds without divesting their long-term assets or incurring significant debt. For instance, a company holding a BG might approach a financial institution to monetize it for immediate operational expenses, thereby enhancing liquidity and financial flexibility.
There are several potential benefits associated with the monetization of financial instruments. Firstly, it provides immediate access to capital, which is crucial for companies facing cash flow shortages or seeking growth opportunities. Additionally, monetization helps optimize a business’s balance sheet, improve financial ratios, and strengthen creditworthiness without traditional financing.
Real-world examples highlight the success of monetizing financial instruments. For instance, a construction firm may possess an SBLC as a performance guarantee for a project. By monetizing this asset, the firm can free up cash for new contracts or unexpected expenses, demonstrating how financial instruments can be strategically used to bolster liquidity. Overall, businesses equipped with proper knowledge of financial instrument monetization can significantly improve their financial standing and operational capacity.
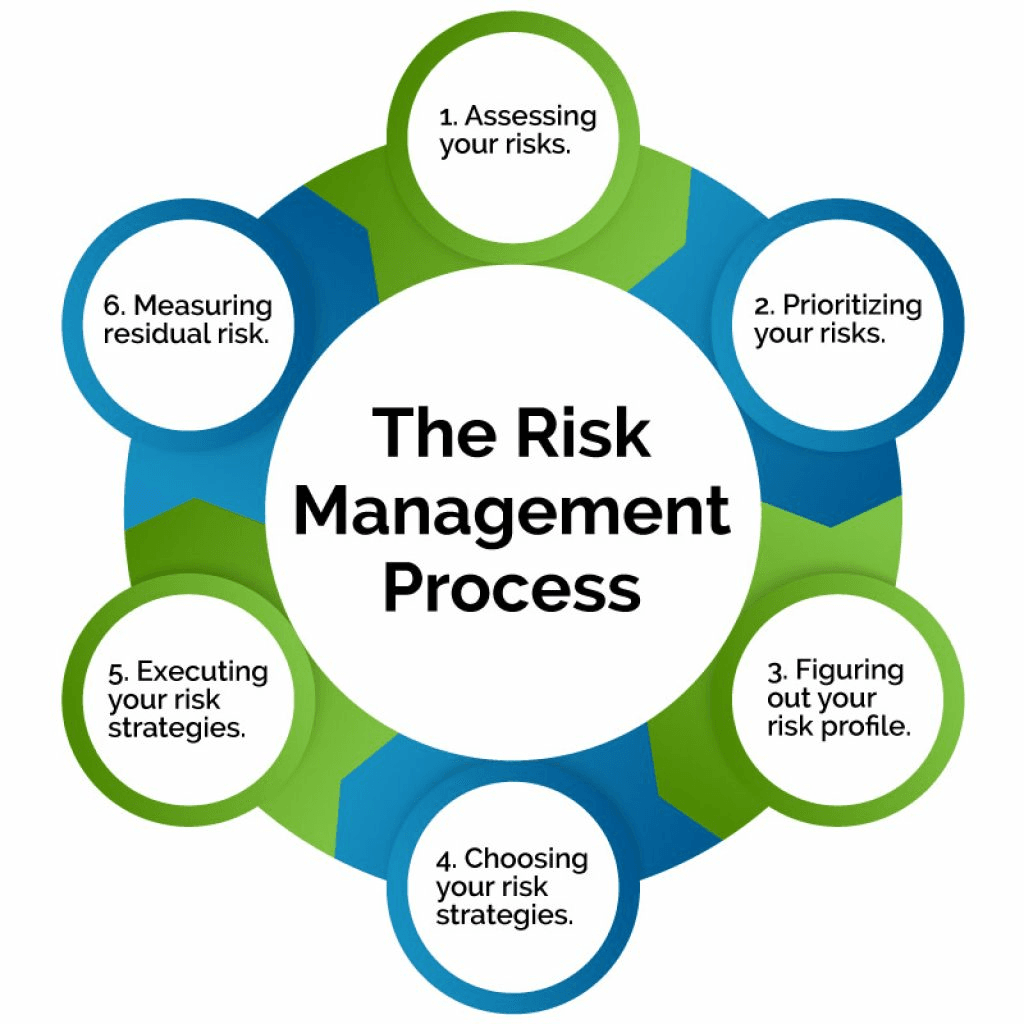
Corporate Financial Solutions and Risk Mitigation
In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade, corporate financial solutions play a pivotal role in managing the multifaceted risks that businesses face. These risks can stem from various factors, such as currency fluctuations, political instability, or credit defaults. By implementing comprehensive risk management techniques, companies can safeguard their investments and maintain cash flow stability. One effective strategy is the utilization of credit enhancement services, which increase the likelihood of receiving timely payments and reduce the potential for losses.
Credit enhancement tools like SBLCs and bank guarantees are key parts of corporate financial solutions for managing risk. An SBLC acts as a safety net, ensuring payment to the beneficiary if the applicant defaults on obligations. Similarly, a bank guarantee offers protection and strengthens the business’s credit profile and credibility with trading partners. These instruments boost creditworthiness and build partner confidence, ultimately helping facilitate smoother and more secure transactions.
Organizations can leverage these instruments to strengthen their financial standing in the international market, minimizing risks associated with trade.
Another key aspect of a robust financial strategy is the effective management of currency risk. Exchange rate variability can severely impact profit margins in international trade. Companies can employ various hedging techniques, such as forward contracts or options, to mitigate potential losses due to unfavorable currency movements. By adopting these strategies, businesses can better navigate the complex waters of global commerce.
In summary, integrating corporate financial solutions with effective risk mitigation strategies is essential for businesses engaged in international trade. Utilizing credit enhancement services and managing currency risk not only protects investments but also contributes to sustained growth and profitability. A well-structured financial approach enables organizations to confidently face the myriad challenges associated with trade finance.
Best Practices for Structured Financing
Structured financing has become an essential tool for businesses, particularly in volatile trading environments. By leveraging various financial instruments, such as Standby Letters of Credit (SBLCs) and bank guarantees, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency and mitigate risks. Understanding the current market trends is vital for successfully navigating structured financing. Recent developments indicate a drift toward more flexible and customizable financial solutions, allowing businesses to align their financing strategies with specific needs and risk profiles.
One of the primary best practices is to conduct thorough due diligence before engaging in any structured financing arrangement. Businesses should evaluate the creditworthiness of their counterparties and ensure they maintain transparent communication throughout the process. This attains a clear understanding of roles, obligations, and expectations, minimizing potential misunderstandings that could lead to financial risks. Furthermore, businesses should continually monitor market conditions, as shifts in economic indicators can impact the performance of structured financial instruments.
A significant pitfall to avoid is over-leveraging or investing in overly complex financial instruments without a clear strategy. Organizations should have a solid grasp of how various structured financing products function and their respective risks. Simplifying structures wherever possible can lead to better comprehension and management of financial exposure. Additionally, businesses operating in emerging markets must carefully assess local regulations and economic conditions that could affect their financing arrangements.
Structured financing plays a pivotal role in providing the liquidity necessary for businesses to thrive, especially during uncertain times. By implementing these best practices, organizations can leverage structured financial instruments effectively while navigating challenges inherent in the trading landscape. The essence of successful structured financing lies in the careful evaluation of risks, aligned with an organization’s broader strategic goals.
Conclusion
When choosing a financial consulting partner, businesses should assess both the services offered and the firm’s trade finance experience. Ascendancy Advisors Limited offers unique expertise, helping businesses make informed decisions and leverage deep knowledge in trade finance.
